
The stethoscope is an essential diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals worldwide. Whether you are a medical student just starting your journey or a seasoned healthcare provider looking to refine your skills, understanding how to effectively use a stethoscope is paramount. In this informative article, we will walk you through the proper techniques of using a stethoscope, highlighting its various parts, positioning, and key tips to enhance your auscultation skills. With a neutral tone and a focus on providing practical insights, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to confidently and accurately listen to the sounds of the human body.
Choosing the Right Stethoscope: A Guide for Beginners
Stethoscope Basics: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using a stethoscope may seem daunting at first, especially if you’re a beginner in the medical field. However, with a little practice and understanding of the basic techniques, you’ll be able to confidently use this essential diagnostic tool. Whether you’re a medical student, nurse, or just interested in learning more, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use a stethoscope.
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Stethoscope
Before you can start using a stethoscope, it’s important to understand its different parts. Familiarize yourself with the earpieces, tubing, chest piece, and diaphragm. Adjust the earpieces to fit comfortably in your ears and ensure that the tubing is in good condition. Take a moment to inspect the chest piece and make sure it’s clean and free from any debris.
Step 2: Proper Placement on the Chest
To use a stethoscope effectively, you need to know where to place it on the patient’s chest. Position the chest piece directly over the area of interest. For example, if you’re listening to the heart, place it on the left side of the chest, slightly below the nipple line. If you’re examining the lungs, position the stethoscope on the back, between the shoulder blades. Take your time to find the correct placement for accurate results.
Step 3: Listen Mindfully
Now that you have the stethoscope in the right position, it’s time to listen carefully. Place the earpieces in your ears and apply gentle pressure with the chest piece on the patient’s chest. Try to eliminate any background noise by asking the patient to remain still and quiet. As you listen, focus on the specific sounds associated with the area you’re examining. For example, listen for the lub-dub of the heart or any abnormal lung sounds.
Step 4: Interpret the Sounds
After listening attentively, it’s crucial to interpret the sounds you hear. Compare them to what is considered normal for that specific region you examined. If you notice any irregularities or unusual sounds, take note of them and consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and diagnosis. Make sure to document your findings accurately for future reference.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to becoming proficient in using a stethoscope. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t be discouraged if it takes a little while to get the hang of it. With time, you’ll develop a keen ear for identifying the intricacies of a patient’s internal sounds, aiding in their diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Stethoscope Components and Functions
In order to effectively use a stethoscope, it is crucial to understand its key components and functions. Let’s take a closer look at the various parts of a stethoscope and how they contribute to its overall functionality.
1. Chestpiece
The chestpiece is the main component of the stethoscope that comes in direct contact with the patient’s body. It consists of the diaphragm and the bell. The diaphragm is a flat, circular surface that is used for listening to high-frequency sounds like lung and normal heart sounds. On the other hand, the bell, which has a larger opening, is specifically designed to detect low-frequency sounds like heart murmurs and abnormal bowel sounds.
2. Tubing
The tubing of a stethoscope connects the chestpiece to the earpieces. It is usually made of high-quality rubber or PVC to ensure optimal sound transmission. Tubing length may vary depending on the type of stethoscope, with longer tubing offering greater flexibility in terms of movement during examinations. It is important to keep the tubing clean and free from any cracks or defects to prevent sound distortion.
3. Earpieces
The earpieces of a stethoscope are designed to fit comfortably in the user’s ears. They are typically made of soft, flexible material that helps in providing a snug fit while reducing external noise interference. Some stethoscopes feature adjustable earpieces to accommodate different ear sizes and preferences. It is recommended to position the earpieces correctly for optimal sound transmission and to prevent discomfort during prolonged use.
4. Binaurals
The binaurals refer to the two metal tubes that connect the earpieces to the tubing. They are responsible for delivering sound from the chestpiece to the user’s ears. Binaurals are usually angled and adjustable to ensure a proper fit and alignment with the ear canals. It is important to adjust the tension of the binaurals to achieve a secure fit without causing discomfort or excessive pressure on the ears.
5. Additional Features
Some stethoscopes may include additional features to enhance usability. For instance, some models may have tunable diaphragms that allow the user to switch between high and low-frequency sounds without changing the chestpiece. Others may have noise-cancelling technology to minimize background noise and improve clarity. It is important to consider these features based on personal preferences and intended use.

Proper Techniques for Using a Stethoscope
Using a stethoscope may seem simple at first glance, but proper techniques are crucial to ensure accurate assessments. Whether you’re a medical professional, a nursing student, or simply interested in understanding more about this essential tool, here are some tips to help you use a stethoscope effectively.
Positioning is key: To begin, it’s essential to position yourself and the patient correctly. Ensure the room is quiet and free from distractions. Have the patient sit or lie down comfortably, exposing the area you need to listen to. Position yourself in a way that allows you easy access to the patient’s body while maintaining a comfortable posture.
Familiarize yourself with the anatomy: Before you dive into using a stethoscope, take the time to familiarize yourself with the human body’s key areas. Knowing where to place the diaphragm or bell of the stethoscope can significantly impact the quality of your auscultation. For example, the diaphragm is commonly used for high-pitched sounds, whereas the bell is ideal for low-pitched sounds.
Use proper technique: When placing the stethoscope on the patient’s body, do it gently and avoid unnecessary pressure. Pressing too firmly may distort the sounds you are trying to hear. Make sure the earpieces fit comfortably in your ears and create a proper seal to block out any external noises. Taking these small but crucial steps will enhance the accuracy of your examination.
Listen carefully: Paying attention to the sounds you hear through the stethoscope is imperative. In addition to differentiating between normal and abnormal sounds, it’s crucial to listen for specific patterns or abnormalities. Be patient during auscultation, and train your ears to detect subtle changes or irregularities. Regular practice and exposure to different patients will refine your listening skills over time.
Clean and maintain your stethoscope: To ensure accurate and safe use, it’s important to keep your stethoscope clean and well-maintained. Wipe down the diaphragm and bell with an alcohol swab after each use to prevent the spread of germs. Additionally, store your stethoscope in a clean, dry place to avoid damage. Regularly checking the tubing and earpieces for wear or cracks will help prolong its lifespan.
Remember, using a stethoscope effectively takes practice and patience. By following these proper techniques, you’ll be able to confidently assess patients’ vital signs and listen for any abnormalities. Finally, always remember to apply your clinical judgment alongside the information you gather through auscultation to provide the best care possible.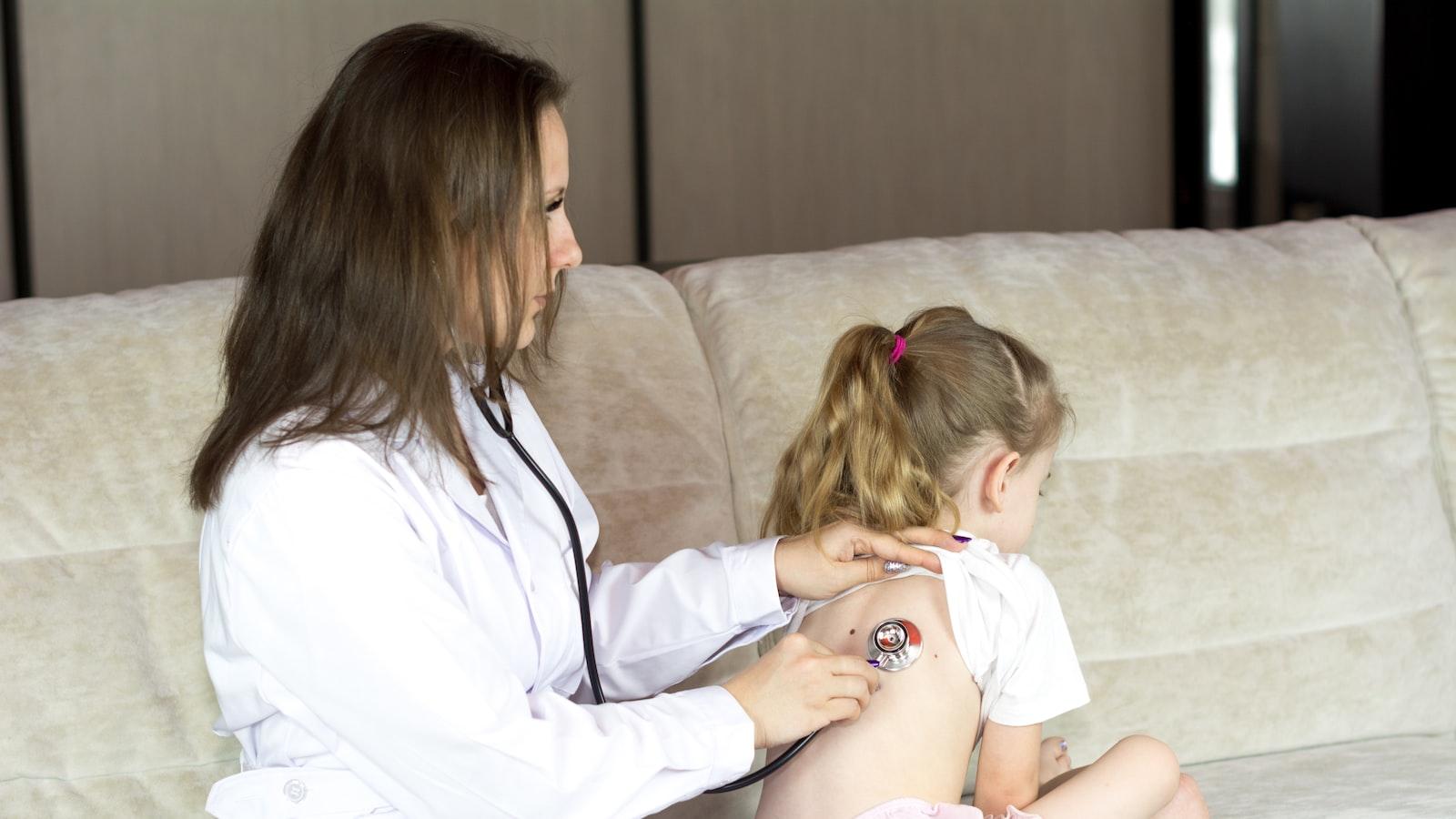
Identifying and Interpreting Body Sounds with a Stethoscope
Introduction
A stethoscope is a vital tool used by healthcare professionals to listen to and interpret body sounds. It consists of a chestpiece, tubing, and earpieces, allowing the user to auscultate various parts of the body. Mastering the art of using a stethoscope is crucial for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of a patient’s health. In this post, we will explore how to effectively use a stethoscope and interpret the different body sounds you may encounter.
The Basics of Using a Stethoscope
Before diving into identifying and interpreting body sounds, it is essential to understand the basics of using a stethoscope properly:
- First, ensure that the earpieces fit comfortably in your ears. Adjust them if necessary to achieve a secure but gentle seal.
- Next, place the chestpiece firmly on the patient’s body. For example, if listening to the heart, position the chestpiece over the left chest wall, slightly below the nipple.
- Make sure the tubing is not twisted or kinked, as this can distort the sound. Keep it free from any clothing interference.
- Hold the stethoscope with a light grip to minimize handling noise and maximize sound transmission.
Identifying Normal Body Sounds
When using a stethoscope, you will encounter a range of normal body sounds. By familiarizing yourself with these sounds, you will be better equipped to identify aberrations and potential abnormalities. Here are some common body sounds you may come across:
| Body Part | Sound |
|---|---|
| Heart | Regular lub-dub sound, representing the opening and closing of the heart valves. |
| Lungs | Soft rustling sounds known as breath sounds, which vary during the respiratory cycle. |
| Abdomen | Gurgling or tinkling sounds caused by the movement of gases and liquids in the intestines. |
Interpreting Abnormal Body Sounds
Accurately identifying abnormal body sounds is vital for diagnosing potential health issues. Abnormal sounds may indicate underlying conditions, such as heart murmurs or lung abnormalities. Here are a few examples of abnormal body sounds you might encounter:
- Heart murmurs: Extra or unusual sounds heard during the cardiac cycle, indicating problems with blood flow through the heart valves.
- Crackles: Discontinuous, bubbling sounds usually heard during inspiration and associated with conditions like pneumonia or congestive heart failure.
- Wheezes: High-pitched continuous sounds typically heard during expiration and indicative of narrowed airways in conditions like asthma.
Conclusion
A stethoscope is an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals, providing valuable insight into a patient’s health status. By familiarizing yourself with the proper technique of using a stethoscope and interpreting body sounds, you can enhance your diagnostic abilities and provide optimal care. Remember, practice and experience are key to master this essential skill.

Maintaining and Cleaning Your Stethoscope for Longevity
One essential tool for medical professionals is a stethoscope. It allows doctors and nurses to listen to the internal sounds of the body, which is crucial for diagnosis and evaluation. To ensure that your stethoscope remains in good working condition and lasts for a long time, proper maintenance and cleaning is necessary. Here are some tips on how to maintain and clean your stethoscope for longevity.
1. Proper Handling and Storage
Always handle your stethoscope with clean hands to prevent any dirt or oils from getting on the diaphragm or tubing. Avoid dropping or accidentally stepping on your stethoscope, as it can cause damage to sensitive components. When not in use, store your stethoscope in a clean, dry place to protect it from dust and moisture.
2. Cleaning the Diaphragm and Ear Tips
The diaphragm and ear tips of your stethoscope come into direct contact with patients, so they need to be cleaned regularly. Gently wipe the diaphragm and ear tips with a soft cloth or alcohol wipe after each use to remove any dirt, oils, or contaminants. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the surfaces.
3. Cleaning the Tubing
The tubing of your stethoscope can accumulate dirt, oils, and bacteria over time. To clean it, use a mild soap solution or a mixture of water and gentle detergent. Dampen a cloth with the solution and gently wipe the entire length of the tubing. Be cautious not to immerse the tubing in water or submerge it, as this could damage the internal components.
4. Inspection and Maintenance
Regularly inspect your stethoscope for any signs of wear, such as cracked tubing or loose ear tips. If you notice any damage, it is essential to repair or replace the affected parts promptly. Some stethoscope manufacturers offer specific cleaning and maintenance instructions, so be sure to follow their recommendations for optimal performance and longevity.
5. Avoiding Contamination
To prevent cross-contamination between patients, it is crucial to clean your stethoscope between each use. Use an alcohol wipe or a disinfectant solution to cleanse the diaphragm and ear tips thoroughly. Additionally, avoid placing your stethoscope on unclean surfaces or letting it come into contact with bodily fluids.
Q&A
Q: What is a stethoscope used for?
A: A stethoscope is a medical instrument primarily used by healthcare professionals to listen to internal sounds within the body, such as the heart, lungs, and bowel sounds.
Q: How does a stethoscope work?
A: A stethoscope works by transmitting sound waves from the chest through hollow tubes to the listener’s ears. It consists of a chest piece, which is placed against the patient’s body, and rubber tubing that connects to earpieces.
Q: How do I properly wear a stethoscope?
A: To wear a stethoscope, place the earpieces gently in your ears, making sure they fit comfortably and provide a good seal. The chest piece should be held firmly against the patient’s skin to avoid any external noise interference.
Q: Are there different types of stethoscopes?
A: Yes, there are different types of stethoscopes available. The most common ones include acoustic stethoscopes, electronic stethoscopes, and fetal stethoscopes. Make sure to choose the one appropriate for your specific field of practice.
Q: How do I clean and maintain my stethoscope?
A: Cleaning and maintaining your stethoscope is crucial to ensure accurate and hygienic examination. You can clean the ear tips and tubing with mild soap and water, but avoid submerging it completely. Regularly check for any cracks or loose parts and have it serviced if necessary.
Q: How do I properly listen to internal sounds using a stethoscope?
A: When using a stethoscope, place the chest piece on the desired area of the patient’s body. Make sure you are in a quiet environment to minimize external noise. Train your ears to differentiate between sounds by practicing regularly and paying attention to nuances.
Q: Can a stethoscope be used on animals?
A: Yes, stethoscopes can also be used on animals. However, it’s important to note that some veterinary stethoscopes have specific features to better suit the needs of veterinarians, such as longer tubing or adjustable chest pieces.
Q: Can I use a stethoscope without medical training?
A: While anyone can technically use a stethoscope, it is important to recognize that proper interpretation of the sounds requires medical training. If you have concerns or want to monitor your health, it is always best to consult a healthcare professional.
Q: How accurate is a stethoscope in diagnosing medical conditions?
A: Stethoscopes are valuable tools in medical diagnosis, but they have limitations. It takes years of training and experience to accurately interpret the sounds heard through a stethoscope. While it can provide valuable clues, additional diagnostic tests may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Q: Where can I purchase a stethoscope?
A: Stethoscopes are widely available for purchase online and in medical supply stores. It’s advisable to consult with a medical professional or read reviews before purchasing to ensure you select a reliable and suitable stethoscope for your needs. In conclusion, mastering the art of using a stethoscope is an essential skill for healthcare professionals. By understanding its components, correctly positioning it on the patient’s body, and interpreting the sounds it produces, practitioners can gain valuable insights into a patient’s health status. Remember to always maintain a neutral and focused approach when using this vital diagnostic tool, as accurate and attentive listening is key. With regular practice, the stethoscope can become an invaluable ally, advancing clinical assessments and aiding in prompt and accurate diagnoses. So, embrace the stethoscope as a gateway into the human body, and unlock the vast symphony of sounds that can unveil important clues about your patients’ well-being.






