In emergency situations, having the knowledge and confidence to use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) can mean the difference between life and death. Understanding the correct procedure for utilizing this life-saving device is crucial, as it can significantly increase the chances of restoring a normal heart rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to use an AED effectively, equipping individuals with the necessary skills to respond swiftly and efficiently in critical moments. By following these guidelines, you can contribute to a higher survival rate and potentially save a life.
Introduction to AEDs and their Importance in Cardiac Emergencies
A cardiac emergency can strike anyone, anywhere, at any time. Therefore, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) and know how to use them effectively. These life-saving devices have revolutionized the field of emergency medicine, greatly increasing the chances of survival for individuals experiencing sudden cardiac arrest.
Using an AED may seem intimidating at first, but rest assured, these devices are designed to be user-friendly, allowing even untrained individuals to provide critical care in a cardiac emergency. When confronted with a cardiac arrest situation, time is of the essence, and every second counts. AEDs are compact and portable, making them readily accessible for use in homes, public places, and workplaces.
To operate an AED, follow these simple steps:
Assess the Situation: First and foremost, ensure the safety of yourself and those around you by evaluating the circumstances. Make sure the person in need is not in a hazardous environment, such as standing in water or near flammable materials. Clear the area to provide ample room for the AED to be used effectively.
Power on the AED: Once the area is secure, power on the AED by pressing the designated button or flipping a switch. Most devices will provide clear audio and visual instructions, guiding you through the entire process. Pay close attention to these prompts as they are designed to assist and reassure you.
Apply the Electrode Pads: Remove the electrode pads from the packaging and carefully place them on the upper right chest and lower left side of the bare chest. Ensure proper placement and firm adhesion to maximize effectiveness. Follow any illustrations or markings on the pads to ensure correct positioning.
Analyze the Heart Rhythm: Once the electrode pads are in place, the AED will automatically analyze the heart’s rhythm. It is vital to stand clear and avoid touching the person during this stage. The AED will determine if a shock is necessary or if it can proceed with other protocols, such as CPR.
Administer a Shock or CPR: If the AED determines a shock is needed, it will charge itself and instruct you to deliver the shock. Follow the device’s guidelines precisely, ensuring that no one is in contact with the person or any conductive surfaces. Alternatively, if a shock is not advised, the AED will guide you through performing CPR until medical professionals arrive.
By familiarizing yourself with the operation of AEDs, you can make a tremendous difference in someone’s life during a cardiac emergency. Remember, these devices are designed to handle the stress and urgency of the situation and will provide clear instructions every step of the way. Spread awareness about the importance of AEDs and be prepared to step up when it matters most.
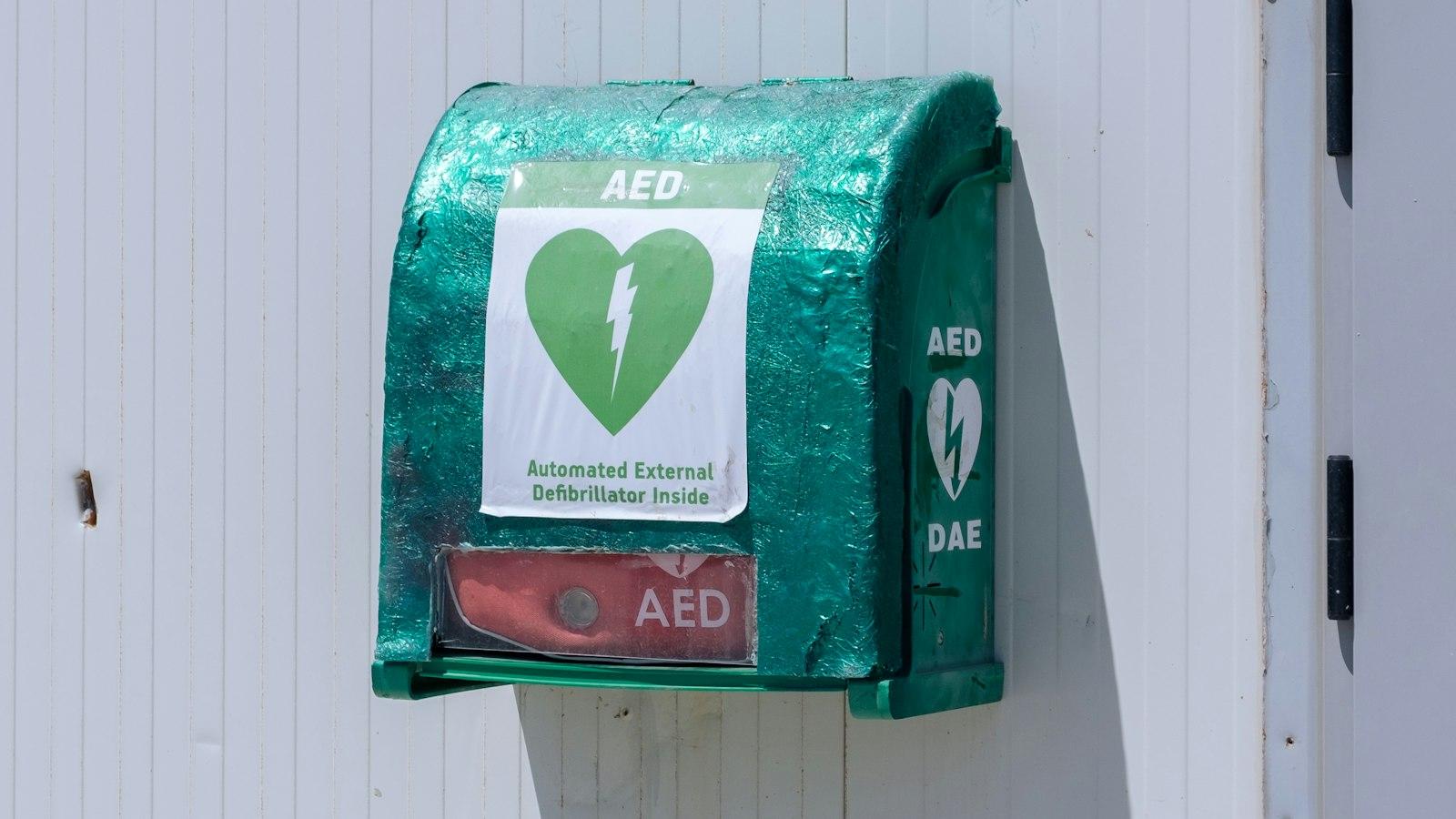

Understanding the Basic Operation and Components of an AED
When faced with a sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) emergency, knowing how to use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) can be the difference between life and death. These portable devices are designed to deliver an electric shock to the heart, helping to restore a normal rhythm. In this article, we will delve into the basic operation and components of an AED, equipping you with the necessary knowledge to confidently use this life-saving device.
Components of an AED
An AED typically consists of four main components:
- Electrode Pads: These adhesive pads are placed on the victim’s bare chest and detect the heart’s rhythm through electrical signals. They also deliver the shock to the heart when prompted by the device.
- Control Panel: The control panel contains the necessary buttons and indicators to operate the AED. These include an on/off switch, electrode pad placement illustrations, as well as voice and visual prompts to guide the user through each step.
- Battery: AEDs are powered by batteries, ensuring their portability and accessibility in any location. It is vital to regularly check the battery life and replace it when necessary to guarantee the device’s functionality.
- Display: The display screen shows the user instructions, visual prompts, and feedback during the rescue process. It allows the user to understand each step and confirm that the device is functioning correctly.
Basic Operation of an AED
Using an AED is simpler than you might think. Follow these straightforward steps:
- Power on the AED by flipping the switch and ensure the electrode pads are placed correctly on the victim’s chest as indicated on the illustrations.
- The AED will automatically analyze the victim’s heart rhythm and determine if a shock is required. It is crucial to ensure nobody is touching the victim during this analysis.
- If the AED advises a shock, ensure everyone is clear of the victim, and press the shock button when prompted. The device will deliver the appropriate shock to the heart.
- After the shock, the AED will instruct you to resume CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) until emergency medical services arrive. Remember to follow the guided prompts provided by the device.
- Continue to follow the AED’s instructions until trained medical professionals take over or until the victim shows signs of regaining consciousness and normal breathing.
Key Considerations
It is important to remember several key considerations when using an AED:
- Ensure the victim’s chest is dry, clean, and free of obstruction to maximize the electrode pad’s efficacy.
- Do not use an AED on infants under one year of age. For children between one and eight years old, utilize pediatric-specific electrode pads if available.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions, as different AED models may have slight variations in operation and pad placement.
- Regularly inspect the AED to ensure it is maintained, accessible, and ready for use in an emergency. This includes checking for visible damages, a functioning battery, and unexpired electrode pads.
With this knowledge of the basic operation and components of an AED, you can confidently assist someone experiencing sudden cardiac arrest until professional help arrives. Remember, quick and efficient use of an AED in a cardiac emergency can truly save lives.

Step-by-Step Guide on Using an AED Safely and Effectively
An AED, or Automated External Defibrillator, is a life-saving device that can be used to aid someone experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. With the proper knowledge and understanding of how to use an AED, you can significantly increase the chances of saving a person’s life. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use an AED safely and effectively.
Step 1: Assess the Situation
Before using an AED, assess the situation for safety. Ensure that the victim and the rescuer are not in immediate danger. If the area is safe, proceed with the following steps.
Step 2: Power On the AED
Locate the power button on the AED and turn it on. Listen carefully for any voice prompts or instructions provided by the device. These prompts are designed to guide you through the entire process.
Step 3: Expose the Chest and Attach the Pads
Remove or cut through any clothing that covers the victim’s chest. Open the AED pads package and carefully peel off the protective cover. Place one pad on the upper-right side of the victim’s chest and the other on the lower-left side.
Step 4: Analyze the Heart Rhythm
Once the pads are properly attached, the AED will automatically begin analyzing the heart rhythm of the victim. Ensure that nobody is touching the victim and follow the voice prompts provided by the AED. This analysis typically takes a few seconds.
Step 5: Administer the Shock and Perform CPR
If the AED advises delivering a shock, ensure that no one is in contact with the victim and press the shock button as instructed. After delivering the shock, immediately resume CPR by following the AED prompts or performing chest compressions and rescue breaths if necessary.

Tips for Proper Placement of AED Pads and Ensuring Electrical Safety
A properly placed AED pad can make a significant difference in the effectiveness of the device during an emergency. When using an AED, it’s crucial to follow these :
Ensure proper pad placement: The AED pads have specific placement locations on the chest. Look for the diagrams on the pads or follow the instructions provided with the device. Generally, one pad is placed on the upper right side of the chest, just below the collarbone, and the other pad is placed on the left side of the chest, below the nipple. Make sure the pads are firmly attached to the skin and free from any obstructions, such as body hair or excessive sweat.
Positioning for pediatric patients: When treating children or infants under eight years old, use pediatric pads if available. If pediatric pads are not available, use adult pads and place them in the center of the child’s chest and on their back, between the shoulder blades. Adjust the energy settings on the device to the appropriate levels for pediatric use.
Consider special circumstances: In certain situations, you may need to modify pad placement. If the patient has a medical implant or a pacemaker, avoid placing the pads directly over the implant or pacemaker. Instead, position the pads at least one inch away. If the patient has a hairy chest, you may need to quickly shave the area before attaching the pads to ensure good contact with the skin.
Ensure electrical safety: Before attaching the AED pads, ensure that the patient is not in contact with any water or a wet surface. Dry the chest if necessary, as water can conduct electricity and potentially cause harm. It’s essential to remove any sources of electricity, such as a puddle or wet surface, to minimize the risk of electrical shock to the rescuer or bystanders.
Monitor the patient and follow prompts: Once the AED pads are in place, the device will give voice and visual prompts to guide you through the process. These prompts will instruct you on when to analyze the heart rhythm and when to deliver a shock if necessary. It’s crucial to stay calm, listen to the prompts, and follow the AED’s instructions carefully.
Remember, the proper placement of AED pads and ensuring electrical safety are critical during an emergency situation. By following these tips, you can confidently use an AED to potentially save a life.
Key Considerations for Responsibly Maintaining and Inspecting AEDs
Using an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) can be a crucial step in saving someone’s life during a cardiac emergency. However, it is equally important to responsibly maintain and inspect these life-saving devices to ensure they are ready for immediate use when needed. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
1. Regularly check the battery and electrode pad expiration dates: AEDs have specific battery and electrode pad expiration dates, which must be regularly checked and replaced if expired. By keeping track of these dates and ensuring timely replacements, you can be confident that your AED is always ready to deliver a life-saving shock.
2. Inspect the AED for physical damage: Periodically inspect your AED for any physical damage such as cracks, dents, or loose parts. These can affect its functioning and may prevent it from delivering an effective shock. If you notice any damage, contact the manufacturer or an authorized technician for repair or replacement.
3. Conduct routine self-tests: Many AEDs have built-in self-test functions that automatically check the device’s readiness for use. These tests typically assess the battery status, electrode pad connectivity, and internal circuitry. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to schedule and perform these self-tests regularly.
4. Train designated personnel: Ensure that individuals responsible for the AED’s maintenance and inspection have received appropriate training. Familiarize them with AED operations, including how to monitor device status, interpret error messages, and perform routine maintenance tasks. This training will help ensure timely and accurate response during emergencies.
5. Keep a log of inspections and maintenance: Maintaining a record of all inspections, maintenance, and replacements is essential for monitoring an AED’s performance over time. Document the dates of each inspection, details of any repairs or replacements, and the names of the individuals involved. This log will serve as a valuable reference and provide an audit trail for responsible AED maintenance.
WordPress Table Example
| Inspection Date | Replaced Battery | Replaced Electrode Pads |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 | No | Yes |
| 2022-06-01 | Yes | No |
| 2023-01-01 | Yes | Yes |
Q&A
Q: What is an AED and what is its purpose?
A: An AED, or Automated External Defibrillator, is a portable electronic device used to treat individuals experiencing sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). Its purpose is to deliver an electric shock to the heart in order to restore its normal rhythm.
Q: Can anyone use an AED?
A: Yes, an AED is designed to be user-friendly and can be used by anyone, regardless of their medical background or training. However, we strongly recommend receiving proper CPR and AED training to increase your effectiveness and confidence in a high-pressure situation.
Q: When should I use an AED?
A: An AED should be used when a person is unresponsive, not breathing normally, and has no pulse or heartbeat. This typically indicates a cardiac arrest, where the heart suddenly stops functioning correctly. In such cases, prompt use of an AED can greatly increase the chances of survival.
Q: How do I use an AED?
A: Firstly, ensure the safety of both yourself and the victim. Check for any potential hazards or sources of electricity nearby. Next, turn on the AED and follow the voice prompts or visual instructions provided by the device. Generally, you will need to attach adhesive pads to the victim’s bare chest, which will then analyze the heart’s rhythm. If advised, stand clear and allow the AED to deliver a shock, or if no shock is advised, continue performing CPR until professional help arrives.
Q: Do I need to remove the victim’s clothing before using an AED?
A: Ideally, the victim’s chest should be bare to facilitate proper adherence of the adhesive pads. However, if time is a critical factor or removing clothing is not feasible, you can apply the AED’s pads directly over clothing. Remember, it is crucial to start the life-saving process as quickly as possible.
Q: Can an AED harm the victim?
A: No, AEDs are designed to be safe and can hardly cause harm to the victim. Before delivering a shock, the AED analyzes the victim’s heart rhythm to determine if a shock is necessary. It will only administer a shock if it detects a specific type of rhythm that can be successfully treated through defibrillation.
Q: Are there any risks associated with using an AED?
A: The biggest risk is not using an AED when it is needed. Delaying or not providing defibrillation can significantly reduce the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. Therefore, it is crucial to promptly locate and use an AED when indicated, in combination with performing CPR.
Q: Where can I find an AED?
A: AEDs are typically found in public places such as airports, shopping malls, sports facilities, and even some schools or workplaces. Look for them in easily accessible locations, often marked with visible signs or symbols.
Q: What should I do after using an AED?
A: After using an AED, it is important to inform emergency medical personnel about the situation. Even if the victim is showing signs of recovery, medical professionals should evaluate them to ensure their well-being and provide any necessary follow-up care.
Q: How often should AEDs be inspected and maintained?
A: AEDs should be regularly inspected according to the manufacturer’s guidelines or local regulations. Routine checks typically involve verifying battery levels, expiration dates of electrode pads, and general device functionality. It is essential to keep AEDs properly maintained to ensure their reliability in case of emergency.
Q: Is it possible to damage an AED by using it incorrectly?
A: While it is important to follow instructions and guidelines when using an AED, the devices are relatively robust and built to withstand common misuse or mishandling. Their design prioritizes simplicity and user-friendliness to minimize the risk of errors. Nevertheless, it is crucial to continue promoting AED awareness and proper training to enhance public safety and effectiveness. In conclusion, learning how to use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) could mean the difference between life and death in a sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) situation. This portable and user-friendly device can be easily operated by anyone, regardless of prior medical training. By following a few simple steps, such as ensuring the safety of the victim, calling emergency services, attaching the AED pads correctly, and following the voice prompts, you can provide critical assistance until medical professionals arrive. Remember, time is of the essence in an SCA, and by swiftly utilizing an AED, you greatly increase the chances of restoring normal heart rhythm and saving a life. By familiarizing yourself with the location of nearby AEDs, encouraging their availability in public spaces, and joining training programs to enhance your readiness, you become an essential link in the chain of survival. So, don’t hesitate to be proactive in acquiring this life-saving skill, as you never know when you may be called upon to help save a life.